Pick-and-Place Device from a 3D-Printer
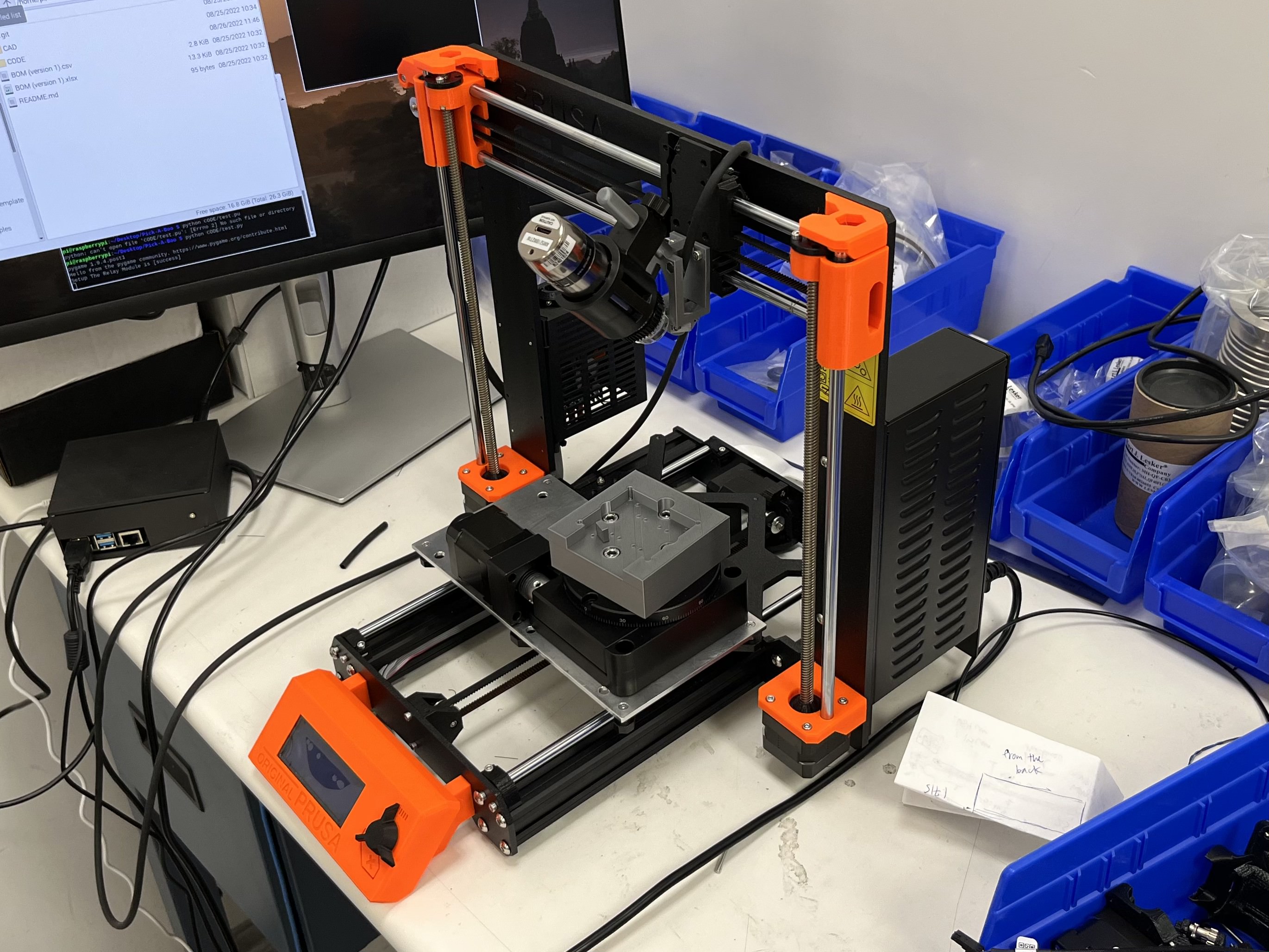

The pick-n-place machine in lab at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Pick-n-place
A pick and place (or pick-n-place) machine is a hardware device typically used for automating the installation of surface mount components on PCBs. They are often also used in the field of experimental physics when precision is required to mount fragile detectors into housings. The downside is that these machines are often prohibitively expensive.
I offered a cheaper alternative to buying a full pick-n-place machine for my research group at SLAC. I designed my own pick-n-place using a 3D printer by borrowing the frame and motor infrastructure from a Prusa i3 MK3S+ 3D printer. I replaced the extruder assembly with a custom suction-head to carefully handle the detector samples, and added a USB microscope camera which allows users to accurately position detectors into their copper housings. The result was a fully-functional pick-n-place capable of mounting devices with micron-level precision.
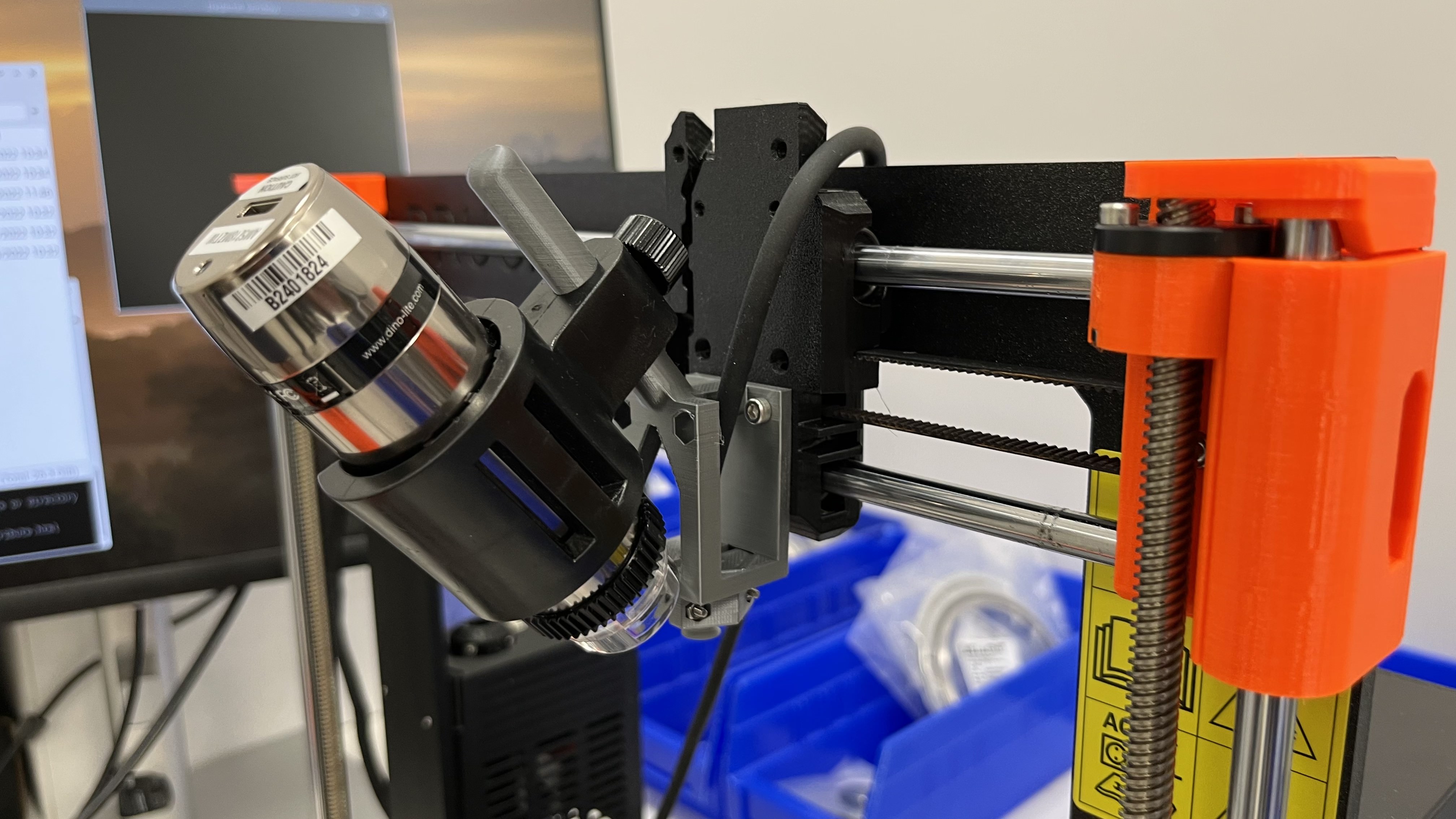 Microscope camera used for high-magnification observation mounted to suction head assembly.
Microscope camera used for high-magnification observation mounted to suction head assembly.
The pick-n-place is controlled entirely from an Raspberry-pi. It handles all of the keyboard inputs to control the machine, and uses a board-mated relay module to toggle a tiny vacuum motor which provides suction. It also handles the stepper motor control of the three steppers providing the translational degrees of freedom native to the Prusa, and an additional single-axis rotation stage mounted on the bed to provide an extra degree of axial alignment.
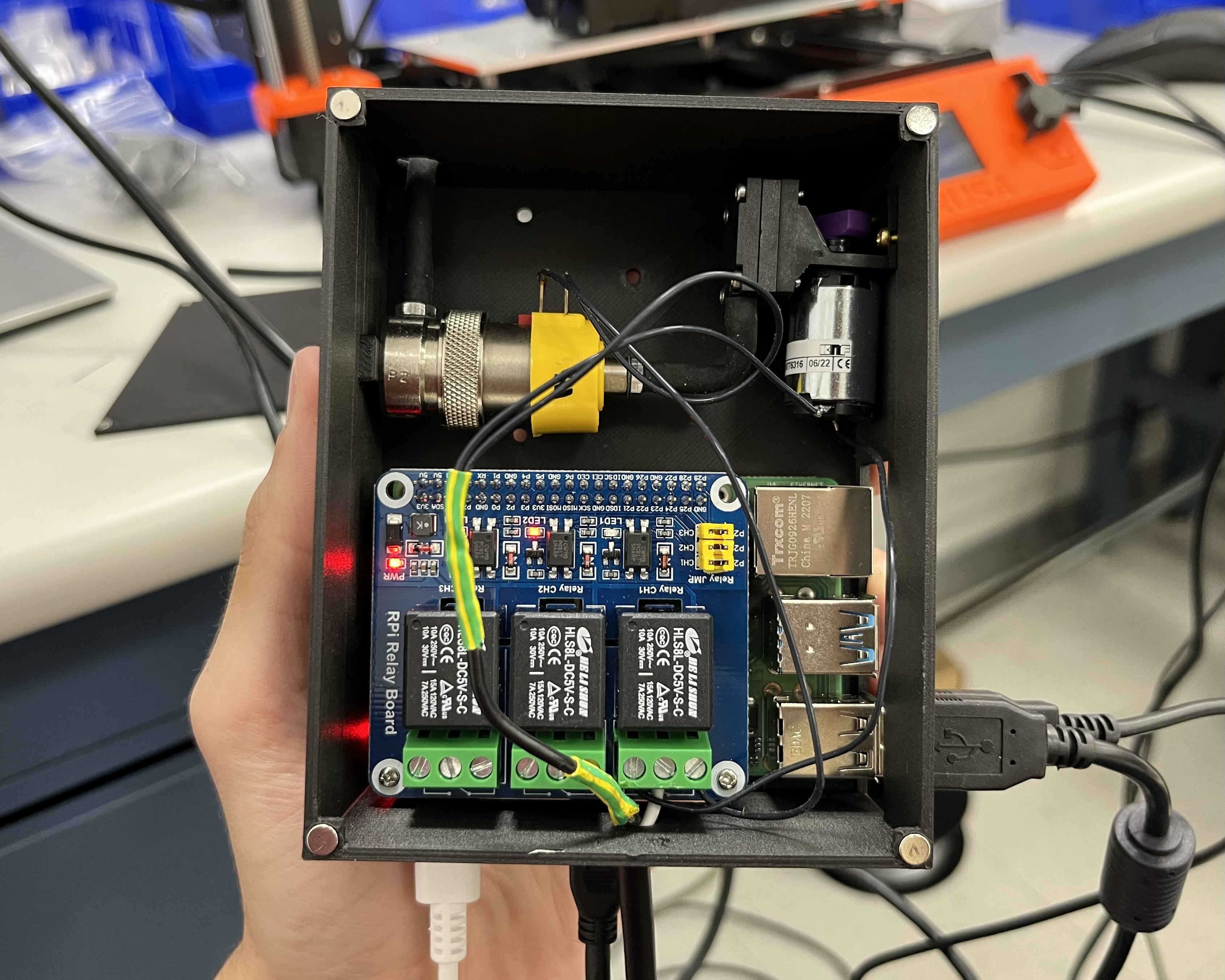 Raspberry Pi control unit and pneumatic suction motor in custom 3D printed case.
Raspberry Pi control unit and pneumatic suction motor in custom 3D printed case.
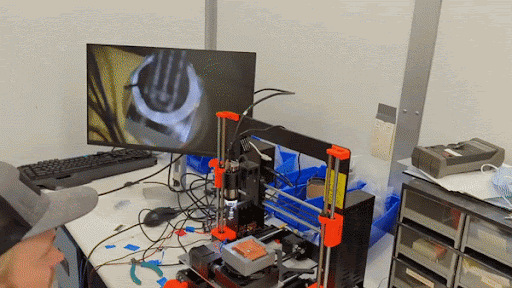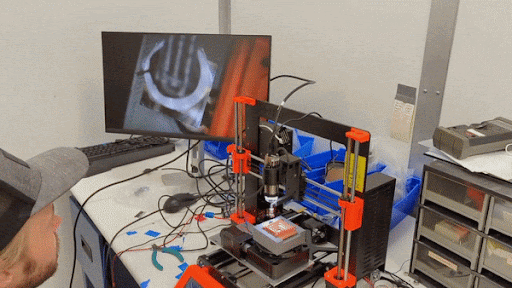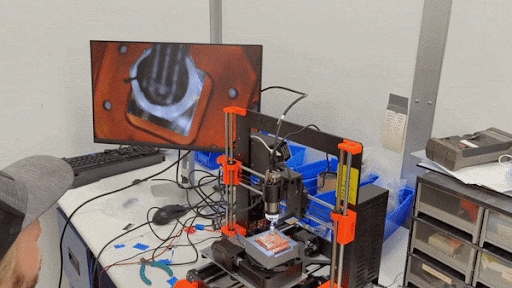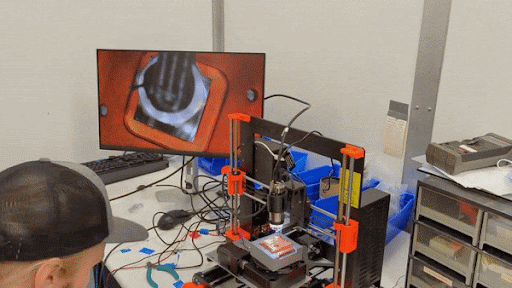 Pick-n-place machine operated by SPLENDOR collaborator Samuel Watkins in the SLAC lab.
Pick-n-place machine operated by SPLENDOR collaborator Samuel Watkins in the SLAC lab.